Inflammation of the prostate (prostatitis) is a very painful condition. But usually prostatitis is not limited to pain and causes even more serious symptoms. Which? How long does prostate inflammation usually last? And what helps?
What is prostatitis?
Prostatitis is inflammation of the prostate (prostate). The prostate can become inflamed as a result, for example, of bacteria that can enter the prostate tissue from the urinary tract. Depending on whether the cause of prostate inflammation is bacterial or not, the following types of prostatitis are distinguished:
- bacterial;
- abacterial prostatitis.
The prostate is a four-centimeter gland, which in men is located under the urinary bladder. It is one of the internal reproductive organs that produces a secretion that mixes with sperm during ejaculation. This secretion ensures the mobility of the spermatozoa and provides support on the way to the female egg.
The prostate in men can become inflamed as a result of inflammation of the bladder or urethra (urethra), and the cause of inflammation can be bacteria that migrate from the bladder or urethra to the prostate. In this case we are talking about acute prostatitis. In most cases, the infection can be controlled with antibiotics.
In about 5 out of 100 patients, the bacteria remain in the prostate despite treatment, leaving the inflammation unchanged. Diagnosis of chronic prostatitis.
Bacteria are not always the cause of prostatitis
Besides bacteria, there are other factors that can cause prostate inflammation, such as central nervous system (CNS) disorders, mental problems, stress, and chronic inflammation of the bladder wall. Because in this case prostatitis occursnot because of bacteria, He calledabacterial prostatitis.
Sometimes abacterial prostatitis is called a form of chronic pelvic pain syndrome (abbreviated as CPPS). However, this pain syndrome can also develop without inflammation of the prostate. In addition to inflammatory, there are also non-inflammatory forms of chronic pelvic pain syndrome.
Note:In non-inflammatory chronic pelvic pain syndrome, the symptoms are similar to those of prostatitis, but neither bacteria nor signs of inflammation are found.
However, in the official classification
prostatitis The US National Institutes of Health lists inflammatory and non-inflammatory forms of the syndromechronically pelvic pain.According to many, this introduces
doctors misleading and in the worst case may lead to inappropriate treatment. Unlike prostatitis, non-inflammatory chronic pelvic pain syndrome does not respond to antibiotic therapy.
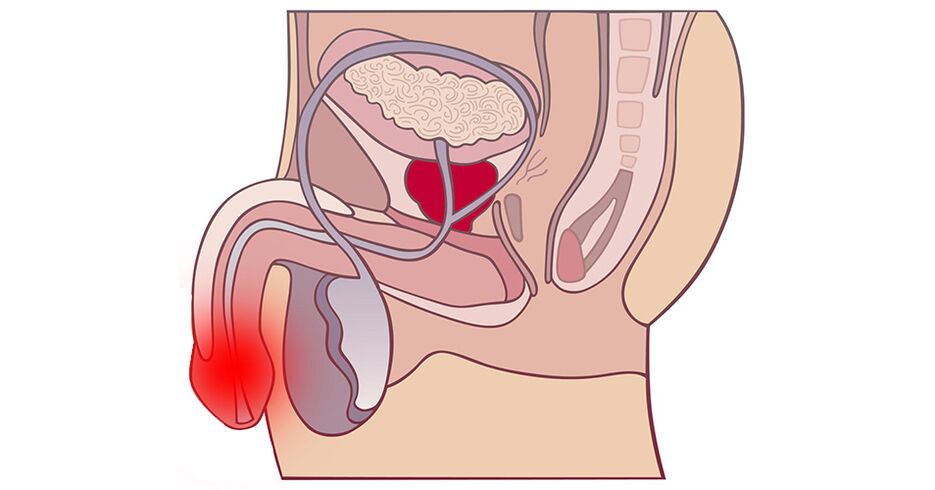
Causes of prostatitis
There are many factors that contribute to inflammation of the prostate. The most important are:
- recurrent infections of the urinary tract;
- bladder catheterization;
- operations in the urogenital area;
- unprotected anal sex.
Under these and other circumstances, bacteria can easily enter the urinary tract and cause inflammation of the prostate. If bacteria enter the prostate, it can lead to bacterial prostatitis.
Abacterial prostatitis can have several causes. Let's take a closer look at the causes of both types of prostatitis.
Bacterial prostatitis
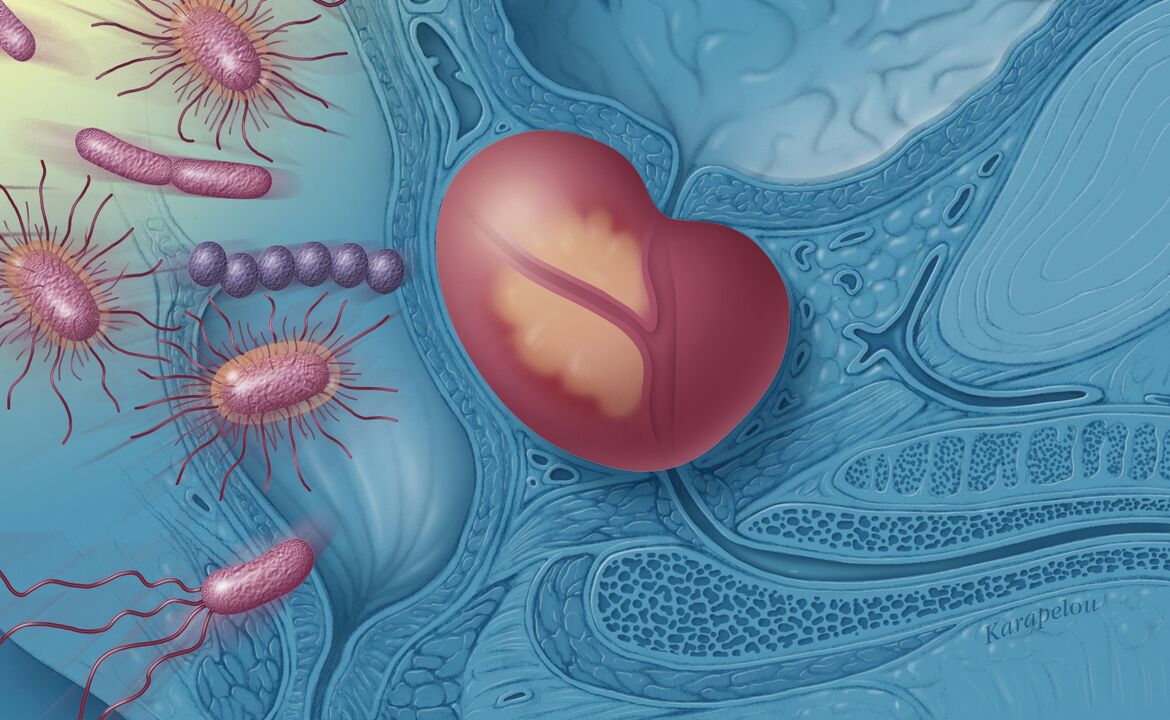
Most bacterial prostatitis is caused by intestinal bacteria such as Escherichia coli or enterococci. If they enter the urinary tract through the opening of the penis, they first cause an infection of the urethra or bladder, and then the pathogens enter the prostate, causing inflammation of the prostate.
Men who develop prostatitis in the hospital often have Pseudomonas aeruginosa. They enter the urinary tract after bladder catheterization.
In rare cases, inflammation of the prostate occurs as a result of sexually transmitted diseases. In this case, the causative agents are mainly chlamydia.
Abacterial prostatitis
In abacterial prostatitis (a form of chronic pelvic pain syndrome), any bacteria can be the culprit. However, after the tests, leukocytes (white blood cells that protect the body) are found in the prostate and sperm. This indicates that the body is fighting inflammation.
What causes this inflammation, experts have not fully understood and studied. This is probably the result of the combined effects of various factors. The following factors may play a role:
- weakened immune response;
- central nervous system disorders that affect the nerves and muscles of the genitourinary system and prevent a person from emptying the bladder as usual;
- mental disorders such as stress, anxiety or depression.
Some experts suggest that hidden infections may be the cause of chronic pelvic pain syndrome. However, this assumption is controversial.
Typical symptoms of prostatitis
Typical symptoms of acute bacterial prostatitis are:
- frequent urination;
- burning during urination (usually with a small amount of urine);
- pain in the bladder and perineum;
- pain during bowel movements;
- nausea, vomiting;
- fever and chills.
Chronic bacterial prostatitis also causes pain and problems with urination. However, these symptoms disappear immediately and then appear after some time. Chronic prostatitis is characterized by a recurrent course with fading and recurrence of inflammation. It can take many months.
Another characteristic sign of chronic prostate inflammation is erectile dysfunction.

Abacterial prostatitis, which is not caused by bacteria, essentially causes symptoms similar to those of chronic bacterial prostatitis. In addition, victims sometimes complain of pain during ejaculation.
Special case: asymptomatic prostatitis
In rare cases, the doctor may detect an increased number of white blood cells in the ejaculate or prostate secretions, but the affected person may not experience pain or other symptoms of prostate inflammation.
Such cases are classified as asymptomatic prostatitis and are usually discovered incidentally as part of screening for cancer or infertility.
Diagnostics
A doctor can diagnose acute bacterial prostatitis by asking the patient about his symptoms and examining the prostate. First, the doctor feels the prostate with his finger. If heat and swelling are felt in the prostate area during palpation, and the patient feels pain, this indicates acute bacterial inflammation.
To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor may also do a urine test and take blood from the patient to examine the level of inflammatory cells.
Chronic bacterial inflammation of the prostate cannot be diagnosed by palpation alone. For example, if the patient is between two bouts of inflammation, the doctor will not be able to detect severe swelling during palpation. Therefore, blood and urine tests are necessary to diagnose chronic bacterial prostatitis.
One urine sample is not enough to detect chronic prostatitis. Because if the urine contains white blood cells and bacteria, it can also indicate a urinary tract infection. To determine whether inflammation is affecting the prostate, your doctor will need to examine several urine samples.
Treatment of prostatitis
Which treatment will help with prostate inflammation depends on the cause: if the inflammation was caused by bacteria, the therapy will differ from the treatment of abacterial prostatitis. However, in both cases, the doctor can prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs (so-called antiphlogistics).
Treatment of bacterial prostatitis
In bacterial prostatitis, antibiotics will help relieve the symptoms.
- In the case of mild acute prostatitis, the doctor must prescribe antibiotics from the fluoroquinolone group, the patient must take them for 10 days.
- If the inflammation is severe, the doctor may give the patient broad-spectrum antibiotics.
- If it is a chronic inflammation, the patient usually takes a fluoroquinolone for 4-6 weeks.
Treatment of abacterial prostatitis
Doctors usually try to control non-bacterial prostatitis using a combination of different drugs. For example, in addition to anti-inflammatory drugs, they can also prescribe the so-calledalpha-1 receptor blockers. They relax the prostate and the muscles of the urinary bladder and thus accelerate the emptying of the bladder.
Depending on your doctor's suspicions about the cause of the inflammation, further measures may be necessary. For example, it has been suggested that psychological problems may also play a role in the development of nonbacterial prostatitis. In that case, the doctor can recommend psychotherapy.
In addition, thermal treatments such as baths can often be used to relieve symptoms.
Treatment of prostatitis with folk remedies
Folk remedies for prostatitis serve as an alternative to drug therapy. It is used for bacterial prostatitis. Before using folk remedies, consult your doctor.
Fireweed
Fenugreek has proven to be an excellent remedy for prostate diseases.
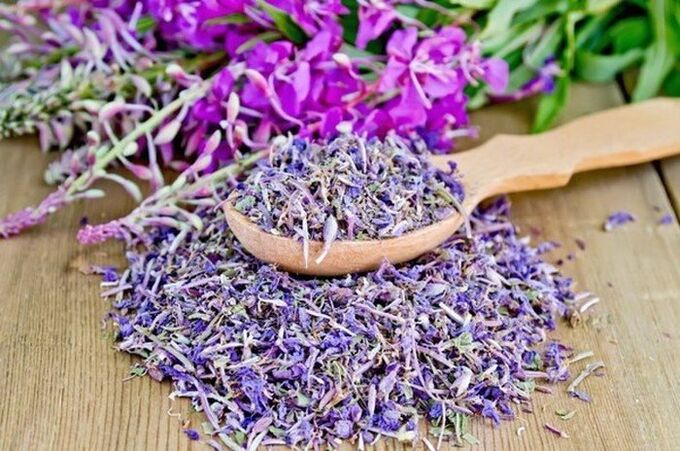

Krovnica is a perennial herbaceous plant. It has small, usually white flowers, but they also come in various shades of red.
The seeds of fire grass are small, on their surface there is a flake with the help of which they spread.
There are about 200 species of fireweed, the plant is often considered a weed and can be very toxic, but beneficial effects have only been shown in fireplaces. Flowers and root are used. The content of biologically active substances (myricetin, kaempferol, quercetin, lectin and sitosterol) has a positive effect on prostate activity.
Uses of fireweed:
Pour 1 full teaspoon of herbs into 1/4 liter of water, boil and let it cook for a short time (15 minutes). Drink it in sips throughout the day (up to 2 cups) chilled.
This medicinal plant is used for various urological diseases, especially:
- for all prostate diseases, including prostate cancer;
- for kidney diseases;
- for diseases of the urinary bladder;
- for bladder cancer;
- for wound healing.
Krovnica is effective against inflammation of the urological tract, as a rule it is combined with other medicinal herbs, depending on the nature of the problem, most often with cranberry, goldenrod, horsetail or birch.
Green tea
Medicines in the form of green tea are probably the most comfortable way to treat prostatitis.
It is recommended to drink 3 cups of green tea a day.
This drink encourages frequent urination, which helps to cleanse the entire body. In addition, green tea is directly involved in the detoxification of the body.
Tip!Men are advised to urinate while sitting. In this way, complete emptying of the bladder is achieved. The sitting position completely releases all pelvic muscles, which is why there is no residual urine in the bladder, where some pathogenic bacteria would otherwise multiply quickly.
Nettles
Pour 2 handfuls of freshly picked nettle leaves - about 15 cm from the top of the plant - with 300 ml of drinking water and leave to stand overnight (approximately 12 hours). In the morning, the infusion should be warmed up a little and drunk.
Cranberry
Cranberry is one of the well-known fighters against prostatitis. Home treatment with cranberry involves consumption in dried, fresh or canned form. In the latter case, however, you should beware of added sugar.
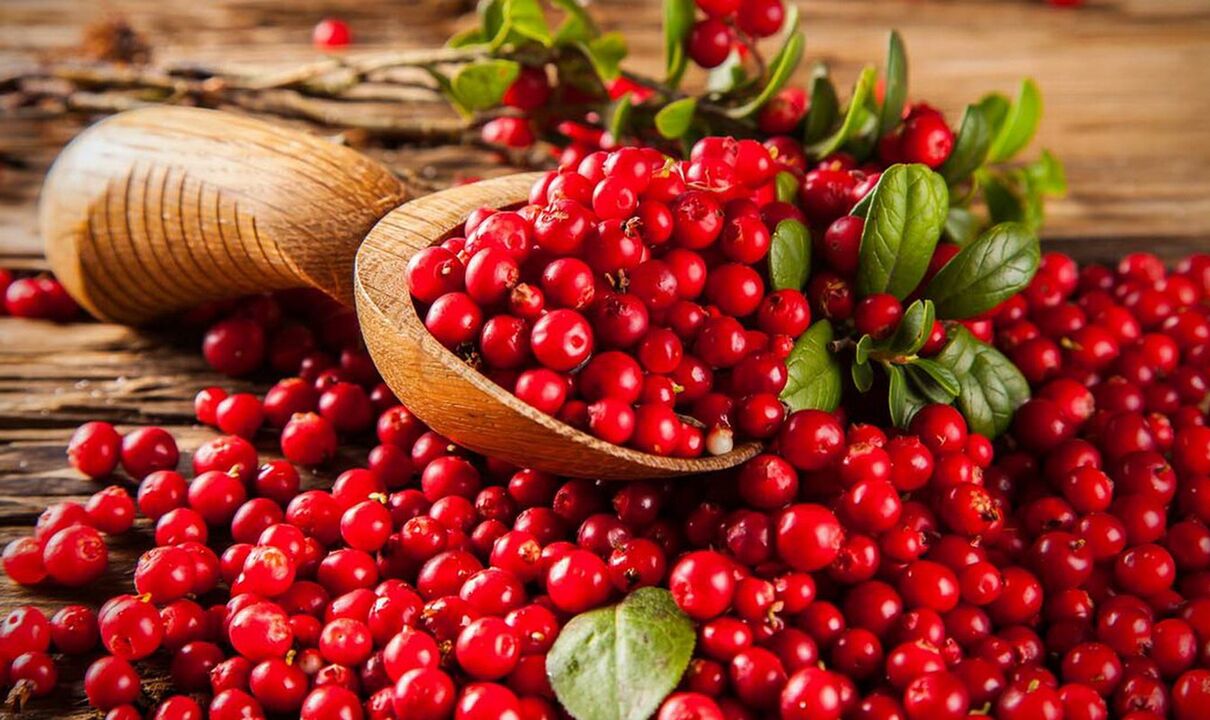

Cranberry juices are also available in stores. You should also be careful here and read the label carefully to make sure that the juice does not contain additional juices from other fruits or artificial sweeteners.
Only 100% cranberry juice has a healing effect.
Add dried cranberries to porridge or oatmeal.
For whom cranberries are not suitable:
Cranberries are contraindicated for people taking blood thinners. Cranberry can reduce the antiplatelet effects of the drug, which will lead to bleeding.
Ginger
When treating prostatitis, you can pay attention to another useful product - ginger root. Ginger is a promising product for the treatment of this disease. It has strong anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, interrupts the reproductive cycle of cancer cells (which is especially important in the treatment of prostate cancer) and promotes apoptosis. In addition, ginger is not toxic to other rapidly growing cells.
It should be taken after meals, adding the root to tea (preferably green).
Pumpkin seeds
As practice shows, the most effective method of treating prostatitis is the use of fresh, not dried, pumpkin seeds.
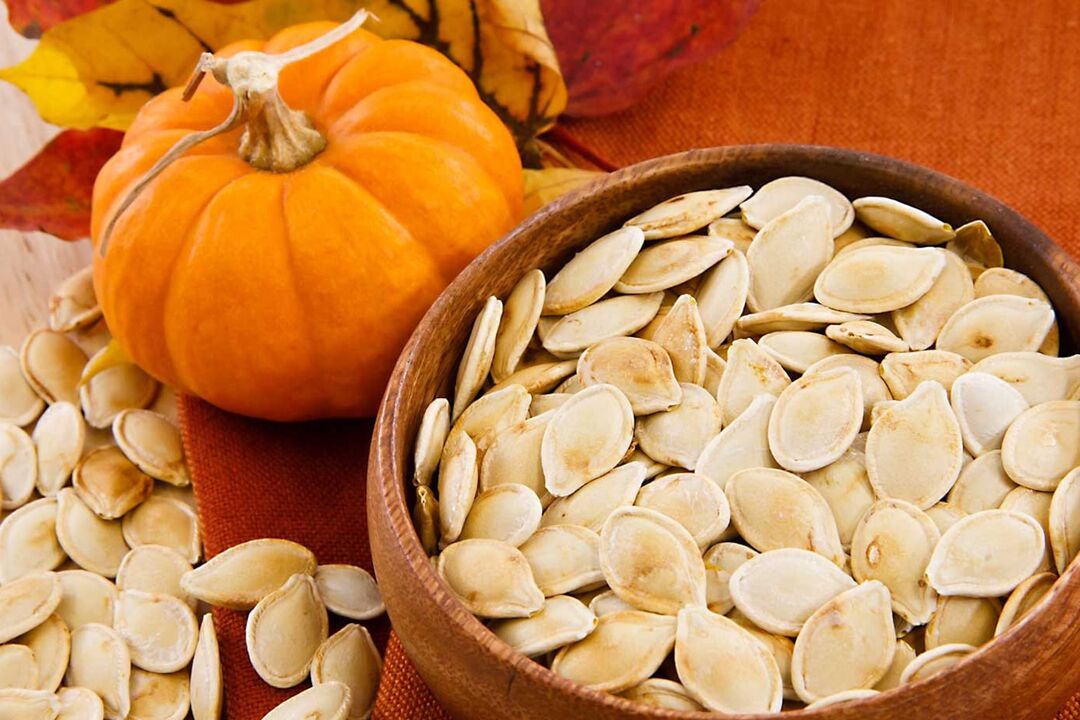

Preparation: Pumpkin seeds should be crushed. The resulting mass is mixed with honey in equal proportions and gently heated. Then it should be left in the refrigerator for several hours, after which it should be shaped into walnut-sized balls.
The balls are taken before meals, 1-2 times a day, daily.
For preventive purposes, you can eat 4-5 pumpkin seeds every day. They contain zinc, selenium and other biochemical substances that reduce inflammation in the body, including the prostate, and have a positive effect on the creation of the male hormone testosterone.
Chestnuts
Chestnut is also effective and has no side effects, which is very important for the elderly.
Peel the chestnuts, crush the kernels into small pieces, pour boiling water over them and leave to stand for an hour.
The decoction should be taken 3 times a day before meals, 30 drops each.
Regular sex
Regular sex, just like masturbation, cleans the prostate, improves blood circulation and prevents local inflammation.
Prognosis: duration and course of prostatitis
Acute prostatitis usually responds well to therapy. If the patient takes the antibiotics prescribed by the doctor, the pain and fever usually disappear within 36 hours. After a few days, the symptoms should decrease significantly.
Chronic prostatitis lasts for several months and usually occurs in relapses, between which the patient feels little or no discomfort. Chronic prostatitis is usually more permanent than acute prostatitis: antibiotic therapy often lasts several weeks.
Is it possible to prevent prostatitis?
Early treatment of urinary tract infections can prevent the spread of germs to the prostate, and thus inflammation of the prostate. Using condoms can also help prevent prostate inflammation caused by certain sexually transmitted diseases.